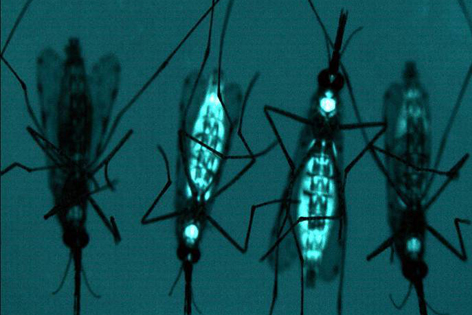
 Do you remember how some scientists, researchers, and individuals like Bill Gates were trying to release genetically modified mosquitoes
into the environment?
Do you remember how some scientists, researchers, and individuals like Bill Gates were trying to release genetically modified mosquitoes
into the environment?
Well, that endeavor isn’t quite over. Two towns
in Northern Australia have recently been gifted with 10-20 thousand genetically engineered mosquitoes – almost completely replacing mosquitoes naturally occurring in the outdoors.
Different Genetically Engineered Mosquitoes?
Although the mosquitoes released are
still GM, they aren’t exactly the same as the more well-known mosquitoes
developed my Oxitec. Oxitec is a British company responsible for the
creation of the genetically engineered mosquitoes containing a gene
designed to kill themselves unless given an antibiotic known as
tetracycline.
The company created this internally manipulated insect to
help control agricultural pests and reduce insect-borne diseases like
dengue fever and malaria.
These new mosquitoes released in
Australia, however, are developed with a slightly different strategy. A
bacterium named Wolbackiapipientis infects numerous insects species, and
harnesses the ability to alter it’s hosts reproductive ability. When
this happens, entire populations become infected within generations, and
when the bacterium infects mosquitoes, the mosquitoes’ ability to pass
on the dengue virus vanishes.
Needless to say, numerous scientists,
researchers, and many individuals have expressed concern regarding the
release of genetically engineered mosquitoes. The first mosquito release by Oxitec took place in
the Cayman Islands in the Caribbean in 2009, only for a second trial to
occur in 2010, where 6,000 mosquitoes were released in Malaysia for
further experiments. Now, 10-20 thousand mosquitoes were released in
Australia, drilling the environment with even more genetically modified creations. As mentioned, many people are not happy about this.
Some individuals, such as Daniel
Strickman, point out the obvious discomfort surrounding the possibility
that the bacterium could become out of control once released – in a way
that does not naturally occur in nature. In addition, mosquitoes less
susceptible to dengue infection could in turn become more susceptible to
other viruses.
Unfortunately, no peer-reviewed scientific proof of the safety of such biotechnologies can be offered. Long-term effects have not
been at all measured, and once these insects are released, they can not
be recalled. Here are but a few of the questions and issues regarding
GM mosquitoes (or any GM insect for that matter).
- Will Oxitec need to acquire the free and informed consent of residents in Key West for the release of the GM mosquitoes? With the previous release of the mosquitoes in the Cayman Islands there was no public consultation taken on potential risks and informed consent was not given from locals.
- What could happen to the ecosystem and local food chain with the major decrease in the Aedes aegypti mosquito population?
- Tetracycline, the antibiotic Oxitec’s genetically engineered mosquitoes are supposed to have no contact with, is showing up in the environment. With tetracycline being present in the wild, these GE mosquitoes would survive and thrive.
- Mosquitoes can develop resistance to the lethal gene inputted by Oxitec. In fact, 3.5 percent of the insects survived to adulthood in laboratory tests despite carrying the lethal gene, according to Todd Shelly, an entomologist for the Agriculture Department in Hawaii.
- 0.5 percent of the released insects are female (the gender which bites humans); what happens to humans if bitten by the female mosquitoes?
- Who regulates releases, and who will be responsible in the event of complications – to any degree?
The truth is that we have no idea what the future holds for genetic modification and the potential impacts it has on the environment and public health.
We know that the genetically engineered mosquitoes are equipped with a
lethal gene designed to lower the mosquito population, but what does
that really mean for humans? We simply do not know the potential
outcomes that could arise from such creations.














.jpg)




































Δεν υπάρχουν σχόλια:
Δημοσίευση σχολίου